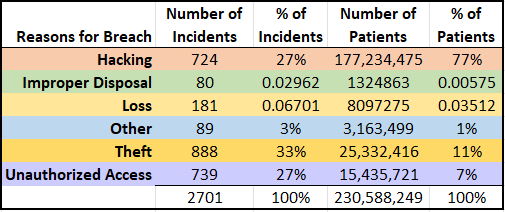
A total of 2,701 breaches have been reported to the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) since 2009, with 138 breaches reported during the third quarter of 2019. Over 230,588,249 patient records have been affected by breaches since 2009 according to the same data. This is a staggering number. For perspective, if these were unique patient records, it would represent approximately 70% of the United States population. A breakdown of all reported breaches, including the reason for the breach can be seen below in Figure 1.
Where are the Healthcare Breaches?
While theft represents a higher number of incidents, hacking is the reason for 77% of all patient record breaches reported to HHS. The data makes is very clear that Protected Health Information (PHI) is highly sought after by cyber-criminals. PHI can be monetized on the Dark Web for an average of $4 – $7 for each record. The value is greater than that of credit cards, for example, because the personal information contained in PHI does not expire, and thus can be used again and again for wrongdoing.
Stop-Gap Measures
In my role as a Security Officer, I tell concerned executives that it is a matter of when, not if their organization will be negatively affected by cyber-events. All hope is not lost, however. There are important steps organizations can take to ensure they are prepared to respond when needed.
Conducting a risk analysis is a vital part of a robust cybersecurity program. This includes a thorough evaluation identifying all threats, controls, vulnerabilities, probability and impact. By conducting a risk analysis, organizations are better positioned to mitigate threats and prioritize their cybersecurity activities.
Ransomware is often reported as a type of Unauthorized Access, and is one of the most ubiquitous attacks. While there are countless ways organizations can design a layered approach to protecting against hacking and ransomware, ensuring their backups are air gapped is an absolute must. This will ensure that if ransomware is successful at infiltrating their environment, their backups will remain unencrypted and thus available.
There is a good deal of focus on password complexity and frequent changes. Current advice suggests that having controls in place that perform a lock-out of accounts after a few failed password attempts is more impactful, however. Two-factor authentication is also a very effective tool to help protect an organization from many cyber threats.
Lastly, organizations are well served by having a security awareness training program in place. Statistics vary, but most show that a large portion of ransomware attacks are the byproduct of a successful phishing attack. One of the most effective ways to drive down the click-rate of phishing emails is through regular staff training. These programs should include internal phishing campaigns where users are exposed to faux-phishing emails and then offered additional education if they are fooled into clicking.
Unfortunately, I anticipate breaches will continue to rise with more people having their PHI exposed. This will slowly change as more organizations are beginning to recognize the importance of investing in their cybersecurity programs, and taking appropriate steps to protect their systems and protected data. Of course, the threats are ever evolving, so organizations will need to remain vigilant if we hope to see a decline in breach activity.
Source: OCR Portal https://ocrportal.hhs.gov/ocr/breach/breach_report.jsf
Credit: Susan Lucci, Sr. Privacy Consultant at tw-Security who performed the data analysis
















Comments are closed.