Embedded analytics, where data analysis occurs within a user’s natural workflow without the need to toggle to another application, has flown under the radar since former Gartner analyst Howard Dresher first used the term in 2007. Prior to the development of newer, more sophisticated embedded analytics software, large quantities of data would be moved from the original software into another program for analysis. Not only was this time-consuming, but it reduced the value of an app because insights were being created elsewhere.
Today’s embedded analytics brings real-time, interactive data visualizations and business intelligence capabilities directly into enterprise applications – creating in-context analytics that improve the usability of data for business users. Over the past decade, we’ve seen major breakthroughs in business intelligence — not only in the way data is collected but also in the software used to analyze it. And those advancements will shape the ways we solve business problems in the future.
According to Research and Markets, the embedded analytics market is growing and will rise to $104.71 billion by 2027. And a recent Infragistics survey, Trends in Software Development and Analytics 2021, found that embedded analytics is currently in use by a third of the software developers and IT leaders in the study. Thirty-three percent of respondents said that the ability to gain a competitive advantage was the key motivation for embedding analytics, while 23% selected “data-driven decision making” as a key motivator. Digital executives need real-time data to make decisions, and business intelligence has become a key tool for interpreting, visualizing, and sharing relevant insights from an organization’s data.
The Importance of Data
Data-driven decision making has never been more important. Applications, and most importantly, embedded analytics — easily supply and analyze useful information which can help drive better informed decisions. From knowing where vaccines are needed to determining marketing budgets, digital executives are relying on data to help them identify challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and make timely decisions that could affect the bottom line.
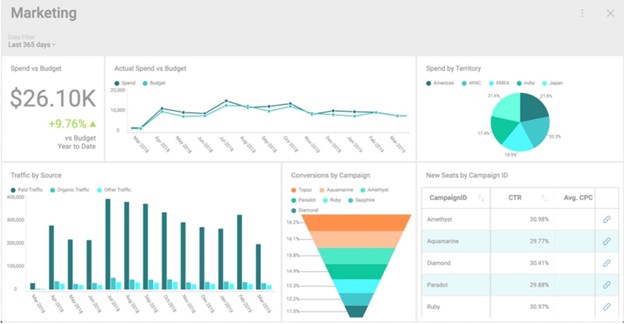
Caption: Embedded analytics software can analyze marketing budgets, including spend, traffic and conversions.
Here are a few of the ways data is used to inform the decision-making process:
- Survey customers to identify trending products, services, and features
- Conduct user testing to identify potential issues before launch
- Understand how a new product or service might perform in a new market
- Analyze demographic data to determine business opportunities and threats
Giving users relevant and timely insights within their workflow promotes a data-driven culture and encourages more analytical thinking. In-context analytics enables your users to make better, faster decisions that are based on the information available at that moment or visible on the specific screen they are viewing. With these insights, users can determine what products are selling, what time of day they are being purchased, and what items are being bought together. Analytics is also a powerful tool for tracking performance, analyzing customer behavior, identifying ways to increase profit, optimizing operations, predicting success, spotting market trends and discovering issues or problems.
Who’s Using Embedded Analytics?
According to Venture Beat, employers are incorporating embedded analytical tools into their talent acquisition programs to expand the pool of potential candidates, identify qualified applicants, and improve the hiring process. Financial services companies use analytics to drill down into data and offer insights to customers.
One powerful use of embedded analytics is the Sensato cybersecurity software, Nightingale. The Nightingale platform provides just-in-time analysis of cybersecurity patterns, threats, trends, and attack analytics. This use of embedded analytics provides cybersecurity analysts with a powerful weapon to utilize against hackers. Embedded analytics can be employed in almost any industry to collect and analyze data, including financial risk analysis, measuring healthcare performance, forecasting manufacturing production, and optimizing grocery inventory levels.
Transforming Data into Meaningful Information
While intuition can be a helpful tool, with data we can utilize data-driven insights to validate a meaningful course of action. We no longer have to rely on gut instincts– we now have the technology to visualize trends and make data-driven conclusions.
Data is a game changer for organizations — big and small. Platforms that transform raw data into scalable and smart insights will continue to grow in popularity. If you’re not taking advantage of data-driven decision-making tools and business intelligence insights, you’re missing the boat.
















