The creative landscape has shifted dramatically in the last few years. I vividly remember the days when creating a simple variation of a concept art piece meant hours of manual repainting or complex Photoshop layering. We would lose days just trying to visualize “what if it were night instead of day?” For digital artists and marketers, the pressure to produce high-volume, high-quality assets is relentless. Research from Adobe, supported by McKinsey’s analysis of the digital shift, indicates that content demand is expected to grow fivefold or more by 2027. This growth is driven by expanding digital channels, hyper-personalization requirements, and always-on campaigns. This is where AI-Powered Visual Transformation, driven by image-to-image technology, has fundamentally changed the creative workflow.
It is no longer just about generating images from scratch using text; it is about refining, restyling, and transforming existing visuals with precision. Through AI-Powered Visual Transformation, creators can maintain the composition of a reference image. At the same time, they can completely overhaul its style, lighting, or texture using image-to-image techniques. As someone who has integrated these tools into professional pipelines, I have seen them bridge the gap between rough sketches and polished deliverables in record time. This article explores how these workflows function. Furthermore, it discusses their practical benefits and how you can master them to unlock new levels of creative potential.
Key Takeaways
- The creative landscape has changed due to rising content demand, pushing artists to adopt AI-Powered Visual Transformation for efficiency.
- Image-to-image technology allows artists to refine and transform existing visuals rather than generate from scratch.
- This method promotes rapid prototyping, enabling creators to explore multiple variations quickly and efficiently.
- Real-world applications include e-commerce product shots, concept art development, marketing visuals, and architectural visualization.
- As the technology evolves, expect real-time interactivity and video integration to enhance creative workflows further.
Table of Contents
Understanding Image-to-Image Fundamentals
At its core, AI-Powered Visual Transformation is a generative process in which an input image serves as the structural foundation for a new output. Unlike text-to-image generation, which pulls concepts from the “latent space” (a compressed representation of data) based solely on words, image-to-image techniques use the pixel data of an uploaded image to guide the diffusion process. Importantly, these techniques also preserve visual structure.
Technically, modern diffusion models work by adding noise to an image until it becomes unrecognizable static, then learning to reverse that process to reconstruct a clear image. Within an AI-Powered Visual Transformation workflow, this process is guided rather than fully random. A reference image that already contains shapes, edges, and composition is provided. The AI is instructed to “denoise” it into a new visual result based on a text prompt.
For example, when a crude pencil sketch is uploaded and paired with a prompt like “hyper-realistic cyberpunk city,” the AI-Powered Visual Transformation system uses the sketch’s lines as constraints. It fills in details according to the prompt while respecting the original boundaries. This enables controlled, predictable generative outcomes rather than arbitrary generation. It is the difference between rolling dice and sculpting with clay: creative control remains with the user, while the AI handles rendering and visual refinement.
Why Image to Image Boosts Creative Efficiency
The primary driver for adopting these tools is efficiency, but it goes beyond speed it is about the fluidity of iteration. In my own projects, I have used image-to-image workflows to cut prototyping phases from days to mere minutes. Before these tools existed, if a client wanted to see a product concept in five different material finishes, I would have to render each one individually in 3D software. Alternatively, I would paint them manually.
Now, I can take a single base render and use image-to-image methods to generate wood, metal, glass, or neon variations instantly. This rapid prototyping capability allows for “fail-fast” exploration. You can discard twenty bad ideas in the time it used to take to produce one mediocre one. Eventually, this leads you to the perfect solution faster.
Furthermore, accessibility is a major factor. You do not need to be a master painter to visualize a high-fidelity concept. By utilizing AI visual editing, a graphic designer can turn a rough collage of stock photos into a cohesive, painted illustration. This democratization of high-end rendering frees professionals to focus on composition, storytelling, and high-level art direction. It also prevents them from getting bogged down in pixel-perfect minutiae.

Real-World Applications for Creators and Pros
The versatility of this technology enables its use across various industries. Based on my observations and industry standards, here are the most impactful ways professionals are deploying these tools:
- E-Commerce and Product Photography: Brands are using image-to-image recontextualization to reframe product shots. A simple photo of a sneaker on a white background can be transformed into a lifestyle shot of the sneaker on a wet city street. Alternatively, it might become a shot on a sunny beach, all without scheduling a location shoot.
- Concept Art and Game Development: Artists use style-transfer workflows to modernize legacy assets or explore new art styles. I often sketch a character pose and use the AI to generate ten different costume variations. The anatomy remains consistent while swapping out the “skin” of the character.
- Marketing and Branding: Marketers can take user-generated content (such as a low-quality phone photo) and upscale or restyle it to align with high-end brand guidelines. This ensures visual consistency across campaigns. At the same time, it avoids rejecting authentic customer photos.
- Architectural Visualization: Architects can feed a rough massing model (a simple blocky 3D shape) into the software and generate photorealistic facade options. This allows them to explore materials and lighting conditions instantly.
In all these cases, the ability to rely on image-to-image ensures the output remains faithful to the original intent while enhancing visual fidelity.
Step-by-Step Workflow for Optimal Results
Achieving professional results requires more than just uploading a picture and hitting “generate.” Through trial and error, I have developed a reliable workflow that maximizes quality and minimizes artifacts.
- Preparation is Key: Start with the highest quality input possible. If you are sketching, ensure your lines are bold and distinct. If using a photo, ensure the lighting is somewhat neutral unless you want the AI to inherit specific shadows.
- Crafting the Prompt: Your text prompt guides the text-guided image changes. Be specific about style, medium, and lighting. For example, instead of just “a cat,” try “cinematic shot, volumetric lighting, 8k resolution, fur texture.”
- The “Denoising Strength” Parameter: This is the most critical setting in any image-to-image tool. It usually ranges from 0.0 to 1.0.
- Low Strength (0.2 – 0.4): The AI sticks very closely to your original image. Use this for slight texture changes or upscaling.
- Medium Strength (0.5 – 0.7): The sweet spot. The AI follows the composition but adds significant new details and style elements.
- High Strength (0.75+): The AI takes creative liberties. It might change the pose, the setting, or the subject entirely, only loosely following the original colors.
- Iterative Refinement: The first result is rarely perfect. I often generate a batch of four images, select the best one, and then feed it back into the image-to-image system as a new input to refine it further. This loop allows you to hone in on the desired look.
By mastering these steps, you move from random generation to intentional creation.
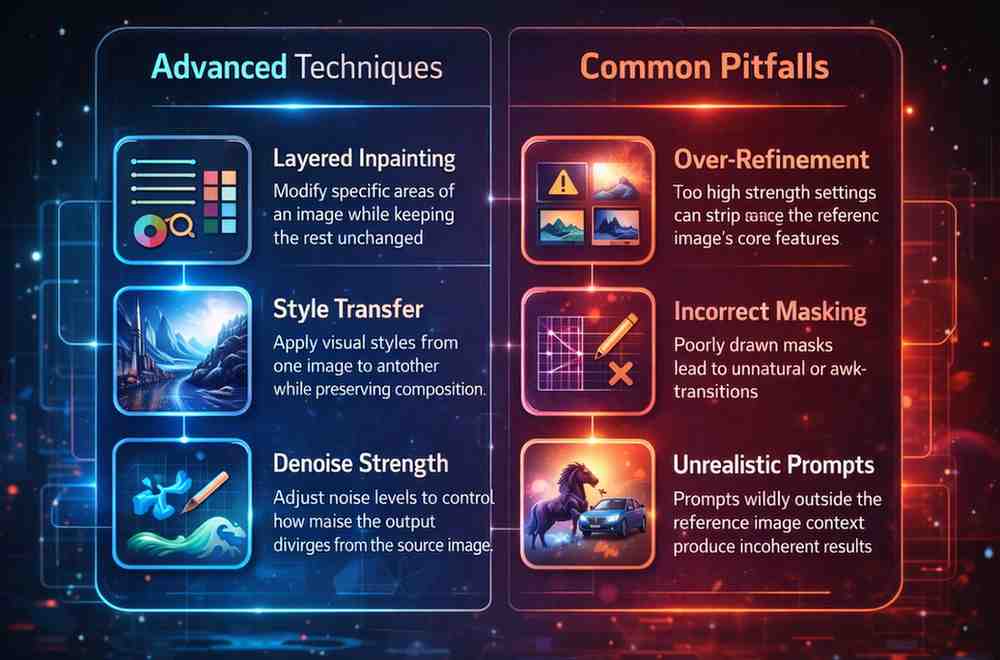
Advanced Techniques and Common Pitfalls
Once you have mastered the basics, you can explore advanced techniques like “inpainting,” which is a localized form of image-to-image. This allows you to mask a specific area, such as a pair of sunglasses on a face, and have the AI regenerate only that section while keeping the rest of the face unchanged. This is crucial for fixing hands or eyes, which generative models notoriously struggle with.
However, there are pitfalls. A common mistake I see is using a “denoising strength” that is too high, resulting in hallucinations where the AI adds extra limbs or distorts perspective because it drifted too far from the reference. Another issue is “burn-in,” where the colors of the original image bleed through too strongly, clashing with the requested style.
Ethically, we must also be mindful of copyright and bias. Research from major AI labs indicates that models can over-represent certain demographics or styles present in their training data. As professionals, it is our duty to use generative transformations responsibly, ensuring we do not infringe on specific artists’ likenesses or perpetuate harmful stereotypes in the content we generate.
The Future of Generative Visual Tools
The trajectory of image-to-image technology is pointing toward real-time interactivity and video integration. We are already seeing prototypes where you can paint on a canvas and see the AI update the photorealistic output in real time, effectively making the “render bar” obsolete.
Furthermore, these techniques are moving into video. Video-to-video processing follows the same principles: it takes a source video and applies style transfer frame by frame. The challenge has been maintaining temporal consistency (keeping the style flicker-free), but recent advancements are rapidly solving this. In the near future, we will likely see full image-to-image pipelines integrated directly into 3D software and video editors, making these AI tools as standard as the “cut” and “paste” commands are today.
Conclusion
The evolution of visual creation is not about replacing the artist; it is about amplifying their intent. As with AI transformation being a challenge of governance rather than capability, the real value lies in how the tools are guided and applied. By integrating image-to-image into your workflow, you unlock a level of speed and experimentation that was previously impossible. Whether you are a hobbyist looking to refine sketches or a creative director managing large-scale campaigns, mastering these tools provides a distinct competitive advantage. I encourage you to experiment, push the boundaries of the settings, and discover how this technology can serve your unique creative vision.