Zero Trust has become the defining security philosophy of modern enterprises, yet real-world environments rarely behave as neatly as architectural diagrams suggest. Production systems evolve unpredictably. Legacy components interact in ways that security teams do not anticipate, identities drift subtly over time, and service accounts that no one remembers, yet continue to authenticate quietly in the background. For any cybersecurity leader operating in this chaotic landscape, deep learning provides an adaptive intelligence layer that sees beyond roles, rules, and static policies. By learning how identities, workloads, and systems naturally behave, deep learning closes the gap between intended design and real operational behavior. Unlike static segmentation or conventional IAM controls, deep learning continually interprets patterns and context—identifying anomalies that humans and rule-based systems routinely miss.
Table of contents
- Technical Analysis
- Where Architecture Assumptions Collapse
- Identity Behavior as Ground Truth
- Behavioral & Deep Learning–Driven Detection Metrics
- Noise Reduction in the SOC
- Hidden Access and Forgotten Identities
- Emerging Trends
- Self‑Healing Segmentation
- Unified Behavioral Graphs
- Autonomous Identity Validation
- Explainable AI
- Conclusion
Technical Analysis
Zero Trust security and deep learning complement one another. Zero Trust defines what should be allowed; deep learning helps determine why behaviors deviate and how risk reveals itself.
Where Architecture Assumptions Collapse
In theory, Zero Trust creates clean segmentation and predictable flows. In reality, deep learning frequently uncovers mismatches:
- Roles that behave inconsistently despite strict IAM definitions
- Service accounts authenticating unexpectedly
- Legacy applications calling deprecated endpoints
- Containers reaching systems outside intended communication paths
- Deep learning accelerates this cycle by flagging deviations immediately instead of waiting for a human audit to find them.
Identity Behavior as Ground Truth
Identity is the strongest signal in a Zero Trust system, but credentials alone cannot guarantee legitimacy. Deep learning strengthens identity verification by analyzing behavior, which is far harder for attackers to fake.
Instead of asking “Is this credential valid?”, modern systems ask:
“Is this identity behaving like itself?”
Deep learning evaluations:
- Timing — unusual login hours or sudden spikes
- Navigation patterns — accessing pages or APIs out of sequence
- Resource traversal — touching systems not normally used
- Volume & speed — rapid data access or automated behavior
- Interaction fingerprints — unique patterns in how users or workloads operate
When behavior deviates from historical norms, the system treats the identity as high risk, even if the credentials are correct. This makes identity behavior the new ground truth for Zero Trust security enforcement.
Field Case Study: The Container That “Almost Looked Normal”
During a hybrid‑cloud migration, one container began making outbound calls to an unfamiliar domain. IAM rules allowed the traffic, so traditional controls stayed silent. Deep learning flagged the pattern instantly. The outbound sequence did not match the container’s historical behavioral profile. Upon investigation, engineers discovered a modified workload image. Deep learning detected malicious intent rather than relying on a static signature.
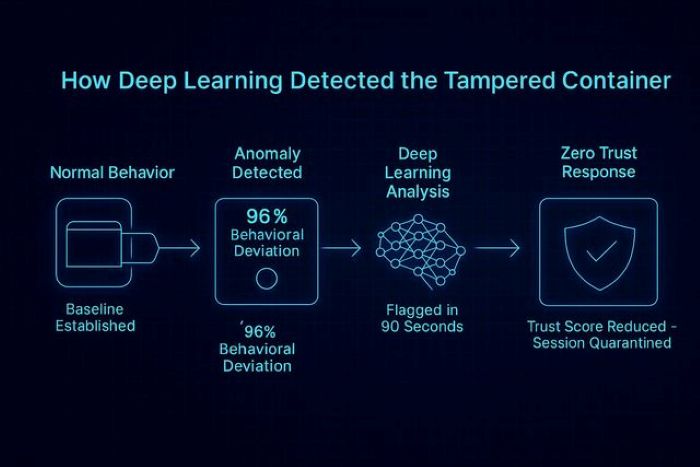
Illustration: How Deep Learning Detected the Tampered Container
Behavioral & Deep Learning–Driven Detection Metrics
| Capability | Improvement / Metric |
| Anomaly Detection Accuracy | 35–60% better detection than rule-based systems |
| False Positive Reduction | 55–80% decrease after baseline stabilization |
| Detection Time | Multi-day detection reduced to < 2 hours |
| Compromised Identity Detection | 4× improvement in detecting misuse / ATO attempts |
| Lateral Movement Visibility | 40–70% earlier discovery of anomalous traversal |
| SOC Analyst Efficiency | 30–50% fewer manual investigations |
| Service Account Drift Detection | 2–3× better anomaly discovery |
| Policy Tuning Speed | 5× faster Zero Trust policy refinement |
Noise Reduction in the SOC
One of the most overlooked benefits of deep learning is noise reduction. As models stabilize, several operational impacts emerge during field rollouts:
- False positive rates drop once baselines mature
- SOC analysts begin to trust model-generated alerts
- Investigation cycles shorten because context is richer
- Downtime and analyst fatigue decrease measurably
By understanding what ‘normal’ looks like across identities, workloads, and services, deep learning suppresses meaningless alerts.
Hidden Access and Forgotten Identities
Months after deployment, deep learning models often surface dormant accounts, neglected service identities, and abandoned privileges. These access remnants are invisible to access reviews yet create enormous risk.
Deep learning models often reveal:
- Dormant admin accounts
- Unused service identities
- Abandoned privileges
- Lateral communication paths no one remembers
These hidden risks rarely appear during annual access reviews but represent some of the most dangerous security blind spots.
Emerging Trends
The intersection of Zero Trust security and deep learning is still emerging. Several major innovations are on the horizon.
Self‑Healing Segmentation
Microsegmentation is moving far beyond static firewall rules and long review cycles. In 2024 and beyond, segmentation will become self-healing, using deep learning to constantly watch how identities, applications, and workloads actually interact.
Instead of waiting for security teams to run audits or clean up outdated rules, these systems will automatically spot unnecessary pathways, overly broad permissions, or risky connections. When something doesn’t make sense like a workload talking to a service it’s never needed before the system can flag it, restrict it, or correct it on its own.
Self-healing segmentation will:
- Understand real traffic patterns and adjust policies as environments change
- Detect when access is too open and automatically tighten it
- Identify unused or risky pathways created during rapid cloud deployments
- Reduce the chance of lateral movement by shutting down abnormal connections in real time
- Learn normal behavior for every workload, not just human identities
Unified Behavioral Graphs
Next-generation Zero Trust security platforms will consolidate human, machine, service, and workload identities into a single, unified behavioral identity graph. Instead of treating these identity types as separate domains, security systems will build behavioral twins, dynamic models that represent how each identity interacts with resources, applications, devices, and other identities.
These graphs will capture every interaction across dimensions such as timing, sequence, privilege usage, communication paths, and anomaly history. The result is a multi-layered risk map that enables security.
Autonomous Identity Validation
In the future, identity security won’t rely on a single “yes or no” decision at login. Instead, trust will adjust continuously based on what a user or system is doing and what level of risk they present at any moment.
Autonomous Identity Validation uses real-time signals—like behavior, device health, location, and current threat activity—to assign a live risk score to every identity. As that score changes, access automatically adapts. If everything looks normal, the system stays out of the way. If something unusual happens, access tightens instantly.
This means:
- Privileges can rise or fall depending on real-time behavior.
- Sessions can be limited or paused when something feels off.
- Machine and API identities are checked just as closely as human users.
- Zero Trust rules are applied continuously instead of only at login.
The result is a living, self-adjusting identity layer that keeps pace with how people and systems actually behave. Instead of chasing threats after they happen, organizations can prevent them by constantly validating trust in the background—quietly, intelligently, and automatically.
Explainable AI
As AI becomes more deeply embedded in real-time access decisions, transparent reasoning is no longer optional—it’s fundamental to trust. Explainable AI (XAI) will provide contextual, human-readable narratives that clarify why a model flagged an anomaly or denied access.
Instead of opaque scoring, security teams will see traceable behavior patterns, contributing signals, historical comparisons, and visual decision paths. This empowers analysts to validate the model’s conclusions, avoid bias, and maintain auditability across compliance frameworks.
Conclusion
Zero Trust offers philosophy; deep learning provides the adaptive intelligence required to operate it. Together, they expose blind spots, reduce noise, highlight intent, and provide defenders with contextual clarity. Organizations that thrive with Zero Trust are not those with the strictest policies, but those that learn continuously from behavioral patterns and evolve security controls accordingly.
In practice, the organizations that succeed with Zero Trust are not the ones with the strictest policies, but the ones that learn fastest from behavioral patterns. Deep learning becomes not just a detection system but a lens that reveals the true dynamics of identity, privilege, and communication across modern ecosystems. Security resilience is built on systems that adapt as quickly as the environments they safeguard. This is where Zero Trust security and deep learning finally converge.
Disclaimer: The insights and perspectives in this article are the author’s own and do not represent any employer. All examples are conceptual and informed solely by independent research and publicly available cybersecurity guidance.











