The intersection of artificial intelligence and IT services represents one of the most transformative shifts in modern business operations. Organizations that successfully integrate AI into their IT infrastructure are discovering unprecedented opportunities for efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage. According to a recent Gartner report, AI-driven automation is fundamentally reshaping the IT services market and forcing service providers to rethink their delivery models. This evolution isn’t merely about adopting new technology; it’s about fundamentally reimagining how businesses deliver value through their IT capabilities.
Table of contents
The Current State of AI in IT Services
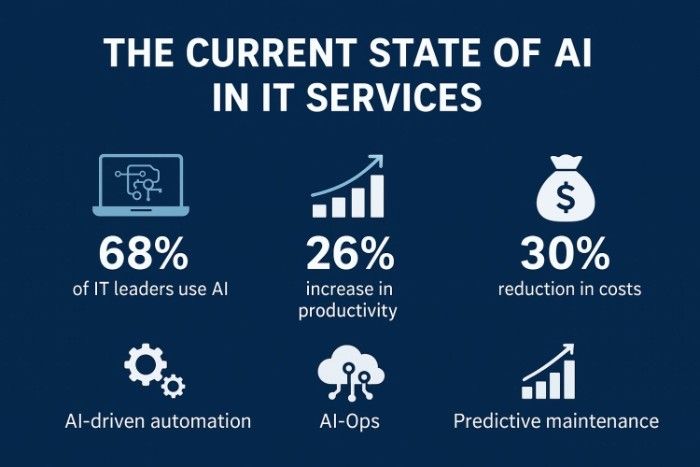
Modern IT departments face mounting pressure to do more with less while maintaining security, reliability, and performance. Traditional approaches to IT service management often struggle with the scale and complexity of contemporary business environments. AI technologies offer a compelling solution by automating routine tasks, predicting potential issues before they escalate, and providing insights that would be impossible to derive manually.
The integration of AI into IT services has matured beyond experimental phases. Machine learning algorithms now power intelligent automation platforms, natural language processing enables sophisticated chatbots for IT support, and predictive analytics help organizations anticipate infrastructure needs. These technologies are no longer futuristic concepts but practical tools delivering measurable business value.
Key Areas Where AI Transforms IT Services
Intelligent Service Desk Operations
The traditional IT service desk has evolved dramatically with the integration of AI. Intelligent virtual agents can now handle a significant portion of routine support requests, from password resets to software troubleshooting. These AI-powered assistants operate continuously, providing immediate responses and freeing human agents to focus on complex issues requiring creativity and emotional intelligence.
Machine learning algorithms analyze historical ticket data to identify patterns, predict common issues, and even suggest solutions before users report problems. This proactive approach reduces downtime and improves user satisfaction while optimizing IT support teams’ workload.
Predictive Maintenance and Infrastructure Management
AI excels at identifying patterns in vast amounts of operational data. When applied to IT infrastructure monitoring, these capabilities enable organizations to shift from reactive to predictive maintenance strategies. Algorithms analyze server logs, network traffic, application performance metrics, and other data sources to detect anomalies that may indicate impending failures.
This predictive approach prevents costly outages and allows IT teams to schedule maintenance during optimal windows. Organizations implementing AI-driven infrastructure management report significant reductions in unplanned downtime and more efficient resource utilization across their technology stack.
Enhanced Security and Threat Detection
Cybersecurity represents perhaps the most critical application of AI in IT services. Traditional security tools struggle to keep pace with rapidly evolving, sophisticated threats. AI-powered security solutions analyze network behavior, user activity, and system interactions in real time to identify suspicious patterns that may indicate breaches or attacks.
These systems learn standard operational patterns and can detect subtle deviations that human analysts might miss. When combined with automated response capabilities, AI enables organizations to contain threats faster and minimize potential damage. The continuous learning aspect of these systems means they become more effective over time as they encounter new threat vectors.
Optimized Resource Allocation and Capacity Planning
Effective capacity planning has always been a challenge for IT organizations. Traditional approaches rely on historical trends and manual forecasting, often resulting in either over-provisioning that wastes resources or under-provisioning that impacts performance. AI transforms this process by analyzing complex patterns in resource utilization across applications, services, and infrastructure components.
Machine learning models predict future demand with remarkable accuracy, accounting for factors such as seasonal variations, business cycles, and application dependencies. This intelligence enables dynamic resource allocation in cloud environments, ensuring optimal performance while controlling costs. Organizations can scale infrastructure proactively rather than reactively, avoiding both performance bottlenecks and unnecessary expenditure.
Intelligent Automation of IT Operations
Beyond simple task automation, AI enables intelligent process automation that adapts to changing conditions and learns from experience. These systems can orchestrate complex workflows across multiple tools and platforms, making decisions based on context and historical outcomes.
For example, when an application performance issue is detected, an AI system might automatically correlate data from monitoring tools, logs, and configuration databases to identify the root cause. It could then initiate remediation workflows, escalate to appropriate teams if needed, and document the incident for future learning. This level of automation dramatically reduces mean time to resolution while ensuring consistent handling of IT operations.
Business Outcomes from AI Integration
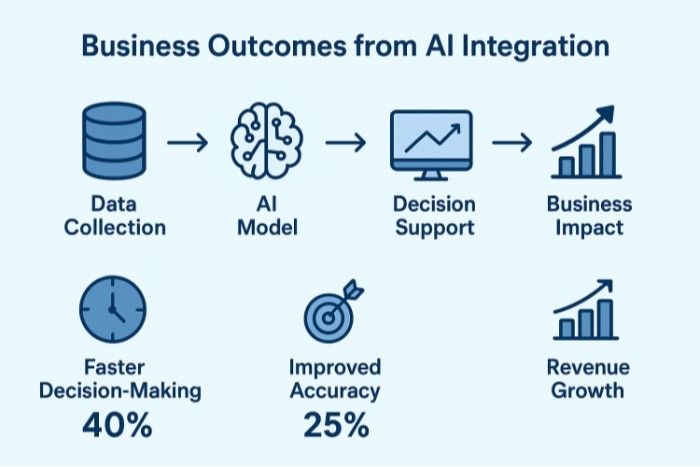
Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
The most immediate benefit organizations experience from AI integration is enhanced operational efficiency. Automating routine tasks reduces the time IT staff spend on repetitive work, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives that drive business value. Studies indicate that organizations implementing AI-powered IT service management tools can reduce operational costs by 20 to 30 percent while improving service quality.
This efficiency extends beyond labor costs. Predictive maintenance reduces expensive emergency repairs and extends asset lifecycles. Intelligent resource allocation optimizes infrastructure spending by ensuring organizations pay only for the capacity they need. The cumulative effect creates significant cost advantages, strengthening competitive positioning.
Improved Service Quality and User Experience
AI integration elevates IT service quality in measurable ways. Faster response times, proactive issue resolution, and personalized support experiences directly impact user satisfaction. Employees spend less time waiting for IT support and more time on productive work, improving overall organizational efficiency.
The consistency that AI brings to service delivery also matters. Automated systems apply best practices uniformly, reducing variability in service quality. This consistency builds trust in IT services and strengthens the perception of IT as a strategic business partner rather than a cost center.
Accelerated Digital Transformation
Organizations pursuing digital transformation initiatives find that AI-enabled IT services accelerate their progress. The agility and scalability that AI brings to IT operations create a foundation for innovation. Development teams can deploy new applications faster, knowing that intelligent systems will monitor performance, detect issues, and automatically optimize resources.
This acceleration creates competitive advantages in markets where speed to market determines success. Organizations can experiment with new services, gather data on their performance, and iterate quickly based on insights that AI systems surface.
Enhanced Decision Making Through Data Insights
AI systems generate valuable insights from the vast amounts of data flowing through the IT infrastructure. These insights inform strategic decisions about technology investments, architectural choices, and service improvements. Leaders gain visibility into patterns and trends that would otherwise go unnoticed without AI-powered analytics.
For example, analyzing service desk ticket patterns might reveal that a particular application consistently generates support requests, indicating a need for additional training or software redesign. Infrastructure analytics might show that specific workloads would benefit from different deployment strategies. These data-driven insights lead to better decisions and more effective resource allocation.
Implementation Strategies for Success
Starting with Clear Objectives
Successful AI integration begins with clearly defined business objectives rather than technology-first thinking. Organizations should identify specific pain points in their IT operations and evaluate how AI can address them. This focused approach ensures that AI implementations deliver measurable value rather than serving as experiments in emerging technology.
Common starting points include automating high-volume, low-complexity support requests, implementing predictive monitoring for critical systems, or enhancing security operations with intelligent threat detection. These focused initiatives build momentum and demonstrate value before expanding to more complex use cases.
Building the Right Foundation
AI systems require quality data to function effectively. Organizations must invest in data management practices that ensure AI algorithms have access to clean, comprehensive, and relevant information. This foundation includes proper logging and monitoring instrumentation, integrated data sources, and governance frameworks that maintain data quality over time.
The technical infrastructure supporting AI must also meet performance requirements. AI-driven cloud services offer compelling advantages for AI workloads, providing scalable computing resources and pre-built AI capabilities that accelerate implementation. These services not only simplify infrastructure management but also enhance efficiency and scalability. Organizations should evaluate their infrastructure readiness and make necessary investments before deploying AI solutions.
Developing Internal Capabilities
While many AI tools come as commercial solutions, organizations benefit from developing internal expertise in AI technologies. This knowledge enables teams to evaluate solutions effectively, customize implementations to specific needs, and integrate AI capabilities into existing processes.
Training programs should target both technical staff who will implement and maintain AI systems and business stakeholders who will use insights generated by these tools. Creating a culture that embraces data-driven decision-making and understands AI capabilities ensures that organizations extract the maximum value from their investments.
Addressing Change Management
AI integration changes how IT teams work, which requires thoughtful change management. Staff may worry that automation will replace their roles, so it’s important to communicate how AI augments rather than replaces human expertise clearly. Organizations that successfully integrate AI emphasize how automation eliminates tedious tasks and allows professionals to focus on more rewarding, strategic work.
Stakeholder engagement throughout the implementation process builds support and ensures that AI solutions address real needs. Regular communication about progress, benefits achieved, and lessons learned maintains momentum and demonstrates ongoing value.
Navigating Challenges and Considerations
Data Privacy and Compliance
AI systems often process sensitive operational and business data, raising important privacy and compliance considerations. Organizations must ensure that AI implementations comply with relevant regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, as well as industry-specific requirements. This includes implementing appropriate data protection measures, maintaining audit trails, and ensuring transparency in how AI systems make decisions.
Privacy-by-design principles should guide AI implementations, minimizing data collection to what’s necessary and implementing strong access controls. Organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions must navigate varying regulatory requirements while maintaining consistent AI capabilities.
Bias and Fairness
AI systems learn from historical data, which may contain biases that affect automated decisions. In IT service management, this could manifest as certain users receiving lower priority or specific types of issues being inadequately addressed. Organizations must actively monitor AI system outputs for bias and implement corrective measures when identified.
Regular audits of AI decision-making, diverse training data, and human oversight for significant automated decisions help ensure fairness. Transparency about how AI systems reach conclusions enables stakeholders to identify and address potential bias issues proactively.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Many organizations operate IT environments that include legacy systems not designed for AI integration. Connecting these systems to modern AI platforms requires thoughtful architecture and, at times, significant integration work. Organizations should prioritize integrations that deliver the highest value while planning longer-term modernization efforts to replace systems that can’t effectively participate in AI-enabled operations.
API-based integration approaches, data transformation layers, and phased migration strategies help organizations bridge the gap between legacy and AI-enabled systems without disrupting operations.
Managing Expectations
AI technologies are powerful but not magical. Organizations sometimes approach AI integration with unrealistic expectations about immediate transformation. Successful implementations require time for systems to learn, for teams to adapt, and for processes to evolve. Setting realistic timelines and celebrating incremental progress maintains stakeholder support through the implementation journey.
Clear communication about what AI can and cannot do prevents disappointment and helps organizations focus on achievable objectives. Pilot projects that demonstrate quick wins build confidence for larger initiatives while managing risk.
Future Trends in AI-Powered IT Services
The trajectory of AI in IT services points toward increasingly sophisticated capabilities. Autonomous IT operations, in which AI systems manage routine tasks with minimal human intervention, are becoming a reality in leading organizations. These self-healing systems detect issues, diagnose root causes, implement fixes, and learn from each incident to improve future responses.
Conversational AI interfaces are evolving beyond simple chatbots to become sophisticated assistants that understand context, remember previous interactions, and proactively offer assistance. These tools will fundamentally change how employees interact with IT services, making technology more accessible to non-technical users.
The convergence of AI with other emerging technologies, such as edge computing, 5G networks, and the Internet of Things, creates new possibilities for IT service delivery. AI will increasingly operate at the network edge, processing data closer to where it’s generated and enabling real-time responses that current architectures cannot support.
As AI technologies mature, the ethical dimensions of their use will receive greater attention. Organizations will need frameworks for responsible AI use in IT operations, ensuring that automation serves human needs and aligns with organizational values.
Conclusion
Integrating AI into IT services represents a fundamental evolution in how organizations leverage technology to gain a competitive advantage. The benefits extend beyond operational efficiency to encompass improved service quality, accelerated innovation, and enhanced decision-making. Organizations that approach AI integration strategically, with clear objectives and proper foundational investments, position themselves to thrive in increasingly digital business environments.
The journey requires commitment, investment, and patience, but the outcomes justify the effort. As AI technologies continue advancing and best practices mature, the gap between organizations that effectively leverage AI in IT services and those that don’t will widen. The time for exploration has passed. The question now is not whether to integrate AI into IT services, but how quickly and effectively organizations can make this transition.
Success in this transformation depends on viewing AI not as a replacement for human expertise but as a powerful augmentation that frees IT professionals to focus on strategic challenges requiring creativity, judgment, and deep business understanding. Organizations that strike this balance between technological capability and human insight will define the future of IT service delivery and reap substantial business rewards.











