When an old web platform starts to struggle to keep up with growth, the automatic reaction is often, “We need to rebuild it from scratch.” But complete rewrites are costly, risky, and might stall your business for years.
Thankfully, with PHP, that won’t be necessary. As the scripting language that initially built Facebook and still runs WordPress and Wikipedia, it can help you modernize piece by piece. You get the benefits of improving security, speed, and stability, without breaking anything.
In this article, we’ll go over the top strategies to use and why deciding to hire PHP developers from DevTeam.Space is the best way to go about it.
Table of contents
Why Scaling is Necessary (And Signs You Need It)
As your business and user base grow, your platform should be able to keep up. Scaling makes sure that your applications don’t buckle under the additional pressure, which might lead to janky customer experiences, decreased satisfaction, and lost sales.
I’m not sure if it’s time to schedule it. Signs that your web app is due for an update include:
- Slower page loads, especially when more users are online
- More frequent downtimes or crashes, like during a product launch or holiday sale
- More user complaints about errors or delays
- More time and money are spent on fixing code to try to address the issues
As soon as you see any of these signs, start looking to hire PHP developers. The earlier you act, the easier it is to reinforce your web apps without total disruption.
6 Ways to Scale Old Web Platforms without Starting From Scratch
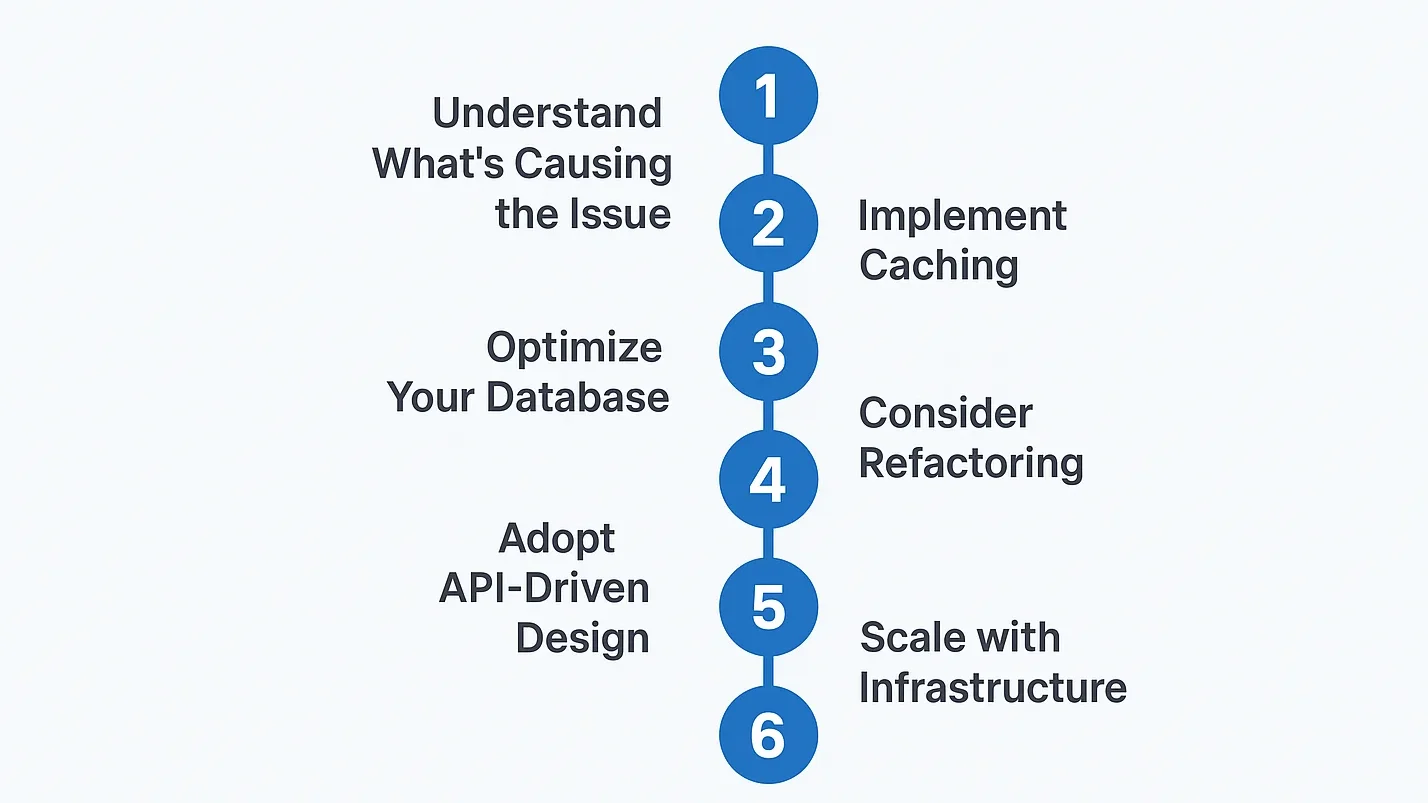
Ready to get started? Here are six top strategies to implement to get your web app performing up to par, without doing a major overhaul.
1. Understand What’s Causing the Issue
The first step in your scaling strategy should be proper issue identification. Many performance issues, after all, boil down to one or two weak spots or bottlenecks, which are areas where users encounter issues.
Most bottlenecks in web apps can be traced to the following:
- The database: poor organization or messy queries can cause delays in information retrieval.
- The code: overly complex or obsolete logic takes longer to run.
- Traffic surges: for servers that are built to handle only light loads, sudden spikes in visitors can overwhelm the system.
When you know which of the above is the point of concern, you can optimize with your partner PHP development team and ensure a speedy, cost-effective, and successful scaling campaign.
2. Implement Caching
Did you know that the simple practice of caching can improve page load time by up to 1000x, according to IBM?
Caching stores the results of everyday tasks or queries so the web app doesn’t need to load them every time a user makes that request. It’s a lot like preparing portions of a popular dish beforehand; when an order comes in, you need to plate the food and serve it, instead of going through the whole hassle of gathering the ingredients and cooking them from scratch every time.
There are different types of caching that you can utilize. The first is page caching, which stores entire pages; the second is database caching, which saves the results of common queries. And the last is object caching, which stores objects, like user profiles or product info.
With caching, your web app can improve performance without requiring massive work.
3. Optimize Your Database
Your database acts as your system’s filing cabinet, storing all the data that it needs to run. When data accumulates, a poorly managed database will inevitably slow down.
Here are some simple ways for optimization:
- Indexing, or creating shortcuts, so the system can quickly find information
- Query optimization, or rewriting inefficient searches to match them to the accurate results faster
- Sharding or replication, which involves splitting the data between multiple servers, so one machine isn’t carrying all the load
Combined with caching, database optimization ensures your system remains efficient, even as usage increases.
4. Consider Refactoring
When platforms evolve, their code often becomes cluttered. This is especially true if you’ve been doing quick fixes or old workarounds to correct issues; years of patching can leave the system fragile and make it difficult to maintain. Sure, the legacy code might still run, but it can be prone to errors and slow down development.
A good way to manage this? You can consider refactoring, which enables you to make minor and safe improvements to your existing codebase. Examples include simplifying complex functions, reorganizing files, or updating outdated practices.
What makes refactoring a particularly effective strategy for PHP apps is that PHP allows old and new code to coexist. You can modernize features gradually, without breaking anything.
For instance, you can improve the search function on your site today, then work on your checkout process next month. It’s seamless and safe.
5. Adopt API-Driven Design
Speaking of working on improvements piecemeal, you can also approach scaling with API-driven design. This way, you can upgrade specific features that require more processing power or specialized handling one by one, rather than slowing down your entire system.
PHP makes this easier by enabling apps to integrate with APIs or external services without issue. You can maintain a stable core platform while also investing in further growth.
6. Scale with Infrastructure

Once your code and features are optimized, you can proceed to scale at the infrastructure level. The infrastructure defines how and where your platform runs, and it’s crucial for proper performance because even the best code can’t handle traffic surges if everything is located on a single server.
Infrastructure scaling can happen as such:
- Cloud hosting: adding resources (such as memory or processing power) during traffic spikes, then scaling back down once demand drops.
- Load balancing: spreading incoming visitors across multiple servers so they’re not concentrated in one server.
- Containers (like Docker): packaging applications into standardized units that can run across different servers or environments.
PHP is highly compatible with any of these modern setups. You don’t need to spend considerable time and money making sure that all the components work together well.
Moving Forward with Scaling
Whichever strategy you opt for, it’s essential to continuously monitor and measure your performance so that you can adjust your approach, as necessary, and spot potential issues early on.
If you don’t have the in-house team to effectively navigate the nuances of scaling PHP applications, you can hire PHP developers to guide you through the process. With their expertise and experience, you can be confident of the success of your scaling campaign.











