CNC laser system not only cuts the materials but also etches and engraves according to your design. Often, etching and engraving are confusing, and difficult to decide which one fits your requirements. The main difference between laser etching vs engraving is that etching uses technology and involves melting material surface to create shallow marks, whereas engraving forms deeper permanent marks. Understanding laser etching and engraving, their capabilities, limitations, and differences is essential to choosing the right method for your application. Let’s discuss those aspects here in this comparative explanation.
Table of contents
What is Laser Etching?
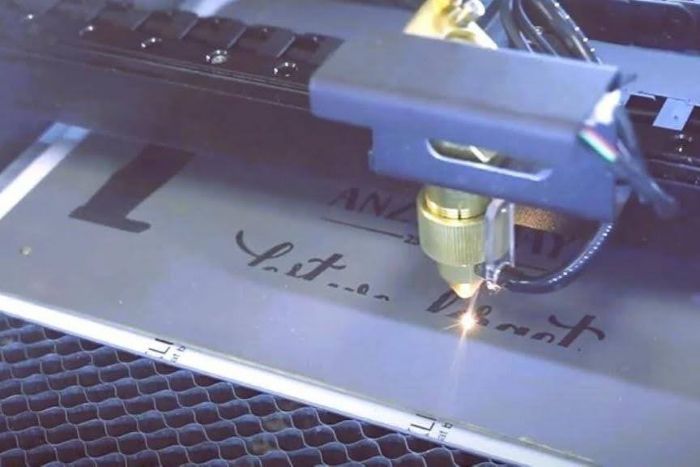
Laser etching is the process of creating high-contrast marks on the material surface by altering the appearance with a laser beam. Instead of vaporizing and eroding, it just melts the material to expand and form a slightly raised mark. The depth of the etched marks typically ranges from 0.025 to 0.125 mm.
It is faster and delivers consistent results across the batches, especially if we compare laser etching vs engraving. Consequently, the laser can etch stainless steel, aluminum, thermoplastic, thermosets, composites, ceramics, etc.
Advantages
- High Speed: Etching marking is faster and more efficient, making it suitable for large volumes.
- Material Versatility: You can etch metals, alloys, plastics, composites, rubbers, ceramics, and fabrics according to the design,
- Etching Colors: Although white and black are the most common etching colors, other different color spectrums can be achieved based on laser and material properties.
- Cost-Effective: In Laser etching vs engraving, etching costs less due to higher production efficiency and speed.
Disadvantages
- Less Durable: The etching marks are less durable than engraving. However, they resist wear at a certain level.
- Restricted Equipment: Some materials require fiber laser machines, which might not be available in all settings.
What is Laser Engraving?
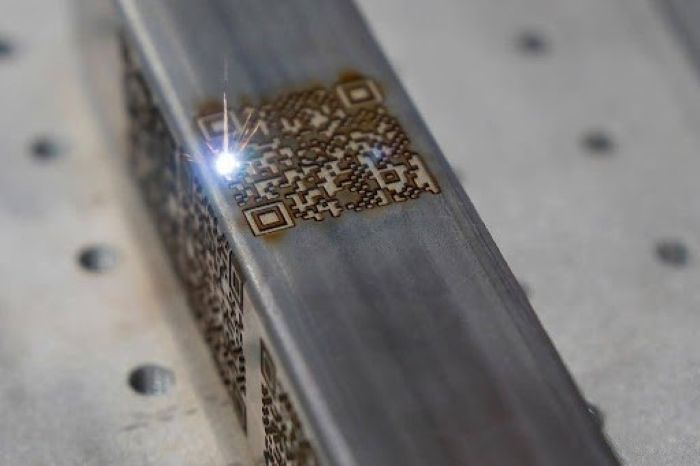
Unlike the laser etching process, engraving involves the use of a high-power laser beam that vaporizes and removes the material from the surface. The depth of engraving is a minimum of 0.125mm and can be higher depending on the work thickness.
Laser engraving creates a clean and detailed design by accurately targeting the material. It can be used for engraving symbols, brand logos, numbers, text, and custom designs. Moreover, custom jewelry also uses engraving for designs and texts.
Advantages
- Highly-durable Marks: The lifespan of the laser engraving marks is the same as parent parts or products.
- Precision: Laser engraving consistently achieves tolerances down to 0.1m ( mostly with metals and plastics).
- Tactile Design: The engraved textures are both visible and touchable.
- Complex Designs Engraving: CNC laser machines are capable of engraving complex designs, such as Gradient shading, micro detailing, and 3D effects.
- Engraving Colors: Without additional painting, laser engraving can alter the surface color via oxidizing, such as white, black, silver, green, blue, and yellow.
Disadvantages
- Time Consuming Process: Detailed material erosion with heat takes more time than etching, adding cost and lead time.
- Material Wastage: It removes substantial material, which might not be suitable for the thin parts.
- High Installation Cost: In the context of laser etching vs engraving, engravers are more expensive.
What are the Major Differences? Comparative Explanation of Laser Etching vs Engraving
Laser etching and laser engraving are fundamentally different regarding how the laser reacts with the material surface. Etching relies on the material’s ability to absorb energy, whereas engraving is about energy concentration.
Furthermore, the table below outlines the major differences in etching vs engraving;
| Aspect | Laser Etching | Laser Engraving |
| Depth of Marking | Shallow (0.025-0.125 mm) | Deeper (0.5-3.5 mm, or more) |
| Speed | Faster (Up to 4 meter/s) | Slower and more detailed (up to 0.6 meter/s) |
| Material Impact | Minimal material removal and preserves integrity | It Removes material, altering surface texture |
| Durability | Less durable as marks are more susceptible to wear | More durable and highly resistant to wear and tear |
| Tactile Feel | Less noticeable to touch | It creates deep and tactile marks |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective | Higher cost due to energy consumption and slower speed |
| Best Use | Surface-level markings on soft materials | Permanent and detailed designs on hard materials |
| Common Materials | Metals, plastics, wood, ceramics, etc. | Metals (e.g., stainless steel), wood, glass, etc. |
Conclusion: Which One Should You Use?
Laser etching vs engraving- the best option for your project depends on the requirements Etching is suitable for applications that require, speed, cost-effectiveness, and large-scale production. But, a mid-level laser precision is okay. On the other hand, engraving is a better choice if you are looking for precision, depth, complexity, and durability. This comparative explanation helps clarify the strengths and limitations of each method. So, consider material type, production volume, and result before making your decision.











