Introduction
In New York’s highly competitive manufacturing landscape, unplanned rework and production delays aresilent profit killers. A single batch scrapped due to design flaws or improper processes not only results in material loss but can also trigger project delays, contract breaches, and cascading costs exceeding 30%. Many companies still rely on outdated manufacturing processes and lack proactive design validation, unable to foresee and mitigate risks before production begins.
This article reveals five innovative practices based on advanced CNC turning Innovations, focusing on preventive optimization from design to final inspection, helping manufacturers fundamentally eliminate rework and delays. Below, we explore how these five strategies, through technological integration and process redesign, can build a robust cost-defense system for New York manufacturers.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- How Can Digital Prototyping with CNC Turning Prevent Design Flaws Before Production?
- Why is mill-turn technology a game-changer for complex part accuracy?
- What Role Does Real-Time Monitoring Play in Eliminating Machining Defects?
- How Does Scientific Tool Management Directly Impact Surface Finish and Tolerance?
- Can Sustainable CNC Turning Practices Actually Enhance Cost-Efficiency?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
How Can Digital Prototyping with CNC Turning Prevent Design Flaws Before Production?
Identifying and correcting design flaws before costly physical machining begins is the first and most critical line of defense against rework. Digital prototyping technology is central to this approach.
1. Virtual machining and Manufacturability Analysis
Using CAD/CAM software as part of modern CNC turning innovations allows engineers to digitally simulate the turning process and visualize potential geometric design flaws, such as tool interference, vibration, or dimensional deviations, before actual machining begins. This preventive optimization resolves issues in the digital environment, significantly reducing physical waste and rework.
2. Adherence to Tolerance Standards
Strict compliance with standards like ASME Y14.5 during the digital design phase is crucial. As emphasized by the Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME) in its discussions on digital manufacturing, early alignment on tolerance understanding significantly reduces ambiguity and risk in production. Validating tolerance allocation in a virtual environment ensures seamless design-to-manufacturing integration.
Why is mill-turn technology a game-changer for complex part accuracy?

For parts with eccentric holes, slots, or complex contours, traditional multi-setup methods are a primary source of error accumulation. Mill-turn technology revolutionizes this by enabling “complete machining in a single setup.”
- Eliminating Datum Transformation Errors: Each transfer of a part from a lathe to a milling or drilling machine introduces new clamping and positioning errors. Mill-turn centers integrate turning, milling, drilling, and even tapping into a single system, fundamentally eliminating cumulative errors and providing unparalleled accuracy for high-precision components such as aerospace parts.
- Representing Best Practices: For complex geometries, advanced CNC turning part production strategies have evolved toward integrated mill-turn machining, which represents today’s best practice. This technological convergence not only enhances precision but also significantly shortens production cycles.
What Role Does Real-Time Monitoring Play in Eliminating Machining Defects?
Detecting defects through post-process inspection often means entire batches are already scrapped. Moving quality control upstream into the machining process is a core advantage of Industry 4.0.
1. From “Post-Process Inspection” to “In-Process Control.”
Sensors installed on CNC turning centers, enabled by modern CNC turning innovations, monitor cutting forces, vibration spectra, and temperature in real time. When data deviates from preset safety thresholds, such as signals of imminent tool failure, the system issues alerts or dynamically adjusts machining parameters. This real-time monitoring shifts quality management from passive detection to active prevention.
2. Alignment with Quality Standards
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) highlights predictive maintenance as key to manufacturing reliability in its innovative manufacturing research. This approach aligns perfectly with process control requirements in standards like ISO 9001, providing New York manufacturers with data-driven decision-making support.
How Does Scientific Tool Management Directly Impact Surface Finish and Tolerance?
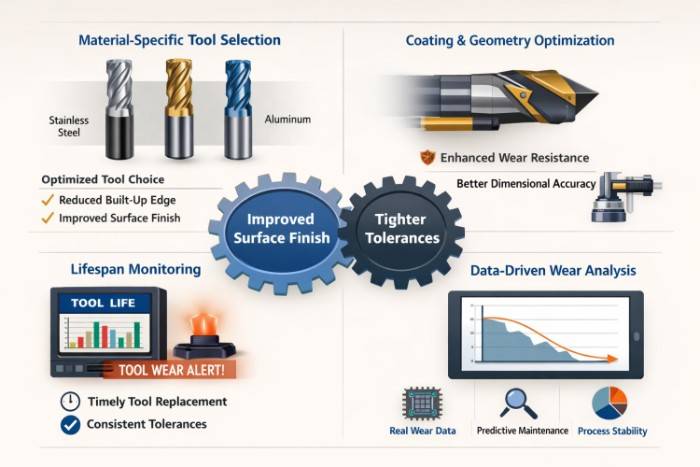
Tools are the “teeth” of the CNC system, and scientific management of their usage directly determines machining stability and quality.
- Scientific Selection Beyond Experience: For different materials (e.g., stainless steel or titanium alloys), tools must be selected based on substrate material, geometry, and coating technology. Optimal choices control built-up edge, improve surface finish, and extend tool life, ensuring process stability.
- Data-Driven Lifespan Management: Replacing tools based on machining time or actual wear data rather than rough estimates prevents dimensional drift caused by tool degradation. Thus, partnering with a full-service CNC turning services provider offers value beyond machining itself, leveraging systematic technical management critical for industries like medical device manufacturing.
Can Sustainable CNC Turning Practices Actually Enhance Cost-Efficiency?
Sustainability is often misunderstood as a mere compliance cost, but it is increasingly becoming a driver of operational excellence.
- Green Practices and Cost Reduction: High-pressure coolant systems boost cutting efficiency and tool life; recycling cutting fluids and metal scrap reduces disposal costs and generates additional revenue. For example, companies certified to ISO 14001 typically integrate these environmental and cost-control measures into lean production models.
- Systematic Resource Management: Sustainable manufacturing practices essentially refine energy and material management. Optimizing tool paths to reduce idle movement and using nesting software to improve material utilization directly lowers operating costs and enhances competitiveness.
Conclusion
Integrating these five innovative strategies, digital prototyping, mill-turn technology, real-time monitoring, scientific tool management, and sustainable practices, enables New York manufacturers to build a highly reliable, efficient, and forward-thinking CNC turning Innovations system. This systematic approach fundamentally mitigates up to 30% of rework and delay risks, transforming cost control from a reactive effort into a proactive strategic advantage.
FAQs
Q1: What is the most common cause of rework in CNC turning projects?
A: The most common cause is often a disconnect between design and manufacturability. Designs with sharp internal corners, unrealistic tolerance expectations, or inadequate consideration of tool access lead to issues that are only apparent during machining, necessitating costly redesign and rework.
Q2: How does mill-turn machining improve accuracy over traditional methods?
A: Mill-turn machining improves accuracy by completing all operations in a single setup. Traditional methods involve moving parts between machines, introducing alignment errors. Mill-turn technology eliminates these cumulative errors, ensuring exceptional precision for complex geometries.
Q3: Can real-time monitoring really prevent all machining defects?
A: While it cannot prevent every defect, real-time monitoring is highly effective against catastrophic failures and batch defects caused by tool wear or process deviations. It serves as an early warning system, allowing intervention before significant scrap is produced.
Q4: What certifications should I look for in a CNC turning supplier to ensure quality?
A: For general quality, ISO 9001 is essential. For automotive components, IATF 16949 is critical; for aerospace, AS9100D is non-negotiable. These certifications demonstrate a supplier’s commitment to a systematic, documented quality management system.
Q5: Are sustainable machining practices more expensive to implement?
A: Initially, investments in equipment like coolant recycling systems may be required. However, sustainable practices typically yield long-term savings through reduced energy consumption, lower waste disposal fees, extended tool life, and revenue from recycled materials.











