Artificial Intelligence (AI) is everywhere whether it’s recommending the next show to binge on Netflix, powering self-driving cars, or responding to customer inquiries through chatbots. But behind many of these smart applications lies a central concept: the AI agent.
So what exactly is an AI agent? Think of it as the “brain” of an intelligent system a digital entity that can sense its environment, make decisions, and take action. In fact, consumers are increasingly open to this kind of intelligent assistance: 39% say they’re comfortable with AI agents scheduling on their behalf, 24% are fine with AI handling shopping tasks, and 44% would use one as a personal assistant, according to recent Salesforce research.
In this article, we’ll explore what AI agents are, how they work, and why they are crucial to the future of technology.
Table of contents
What Is an AI Agent?

At its core, an AI agent is a computer system that perceives its environment and acts upon it autonomously to achieve specific goals. This means it doesn’t just follow a fixed script, it observes what’s happening around it, processes that information, and makes decisions based on logic, rules, or learned experience.
An AI agent might be as simple as a program that turns off your smart lights at bedtime, or as complex as a self-driving car navigating city traffic. What they all have in common is a sense-think-act loop that enables them to function independently.
Key Features of an AI Agent:
- Perception: It gathers information from the environment (via sensors, user input, or data feeds).
- Decision-making: It processes the information to decide what to do next.
- Action: It performs tasks based on its decision (e.g., moving, replying, or sending commands).
- Autonomy: It can operate without constant human guidance.
- Goal-oriented behavior: It acts in a way that moves it closer to achieving its goal.
Some AI agents are also capable of learning from their experiences, making them more innovative and more efficient over time.
Types of AI Agents
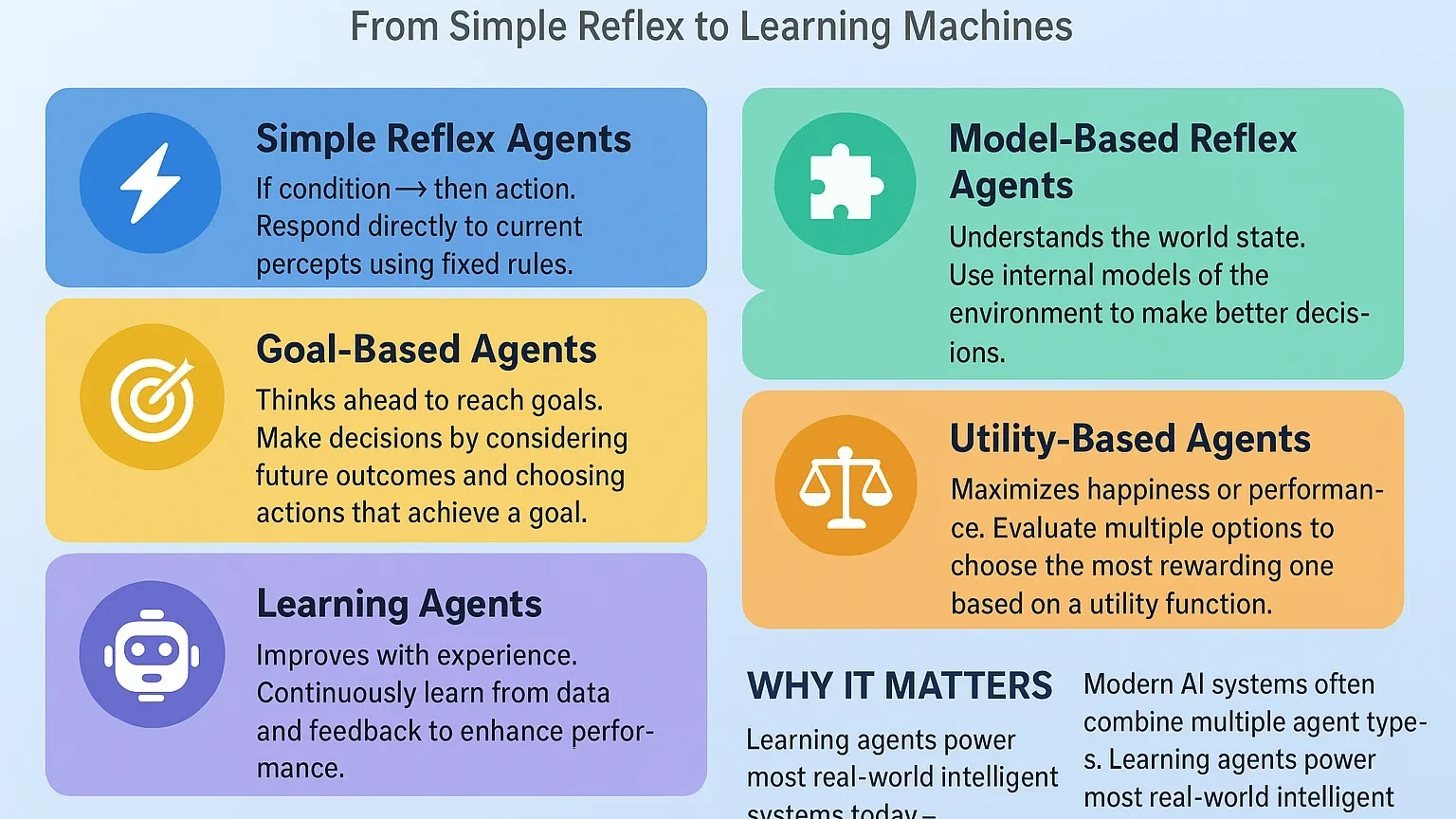
AI agents come in different types, depending on their design and purpose. Here are a few common categories:
1. Simple Reflex Agents
These agents act solely based on the current situation. They don’t consider past experiences or future consequences. A good example is a thermostat that turns on the heater when the temperature drops below a certain level.
2. Model-Based Agents
These agents maintain an internal model of the world to keep track of past events and predict future outcomes. For example, a robot vacuum may map your house to clean efficiently.
3. Goal-Based Agents
These agents make decisions based on specific goals. They evaluate possible actions and choose the ones that bring them closer to achieving their goal. A GPS navigation system is a goal-based agent that finds the best route to a destination.
4. Utility-Based Agents
Instead of just achieving goals, these agents consider multiple factors to make the “best” possible decision. For example, a delivery drone might weigh factors like weather, traffic, and battery life to find the most efficient delivery route.
5. Learning Agents
These agents can learn and adapt over time. They improve their performance by analyzing past experiences. Most modern AI systems, like recommendation engines and language models, fall into this category.
Real-World Applications of AI Agents
They are already embedded in many aspects of daily life and business. Here are just a few examples:
- Virtual Assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant use to understand voice commands, fetch information, and carry out tasks.
- Customer Service Chatbots: These agents handle routine customer inquiries, saving time and money for businesses.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars use a network of them to sense their surroundings, interpret traffic data, and make driving decisions.
- Smart Home Devices: They manage lighting, temperature, and security based on user preferences and environmental inputs.
- Healthcare Systems: Agents assist doctors by analyzing patient data, detecting anomalies, and even recommending treatments.
Why AI Agents Matter

They are essential because they bring the power of decision-making and autonomy to machines. Unlike traditional programs that do only what they’re explicitly told, AI agents can adapt, optimize, and improve traits that are critical in a fast-changing world.
As technology advances, they are expected to take on even more complex roles. In areas like personalized medicine, climate modeling, and space exploration, they will act as trusted digital partners, helping humans solve problems we couldn’t tackle alone.
However, implementing AI agents requires careful planning and resource allocation. Businesses looking to develop custom AI solutions should first understand how much does it cost to build an AI agent to properly budget for development, deployment, and ongoing maintenance.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI agents offer tremendous potential, they also raise important questions:
- Transparency: How do agents make their decisions?
- Bias: Are the agents learning from fair and unbiased data?
- Autonomy vs. Control: How much freedom should we give to AI systems?
- Accountability: Who is responsible when an AI agent makes a mistake?
Developers and policymakers must work together to ensure that AI agents are designed and deployed responsibly.











