Introduction
Industrial engineers in contemporary manufacturing environments are challenged by issues such as quality variation, scrap rates, and cost, particularly when building precision parts. The conventional approach is inefficient for creating parts with micron-level accuracy, leading to failed assemblies and reliability issues. The underlying reason for this is inadequate process control and unorganized quality processes.
In this article, we will discuss precision CNC turning, where the blending of advanced machines, digital processing, and quality control may enable zero-defect manufacturing. Using case studies from various industries, we can provide guidance on how to overcome these challenges. In the next sections, we will discuss the technical concepts so that readers can learn the key areas of precision manufacturing.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- What is Precision CNC Turning and How Does It Differ from Conventional Machining?
- In What Ways Can Advanced CNC Turning Machines Be Used to Obtain Micron-Level Tolerance
- What Are the Key Processes in CNC Turning for High-Precision Components?
- Ways & Methods to Achieve Effective Quality Control in CNC Turning.
- What Role Does Digital Transformation Play in Enhancing CNC Turning Efficiency?
- Ways for Manufacturers to Choose a Trustworthy Partner for Precision Turning Services
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Precision CNC Turning and How Does It Differ from Conventional Machining?
Precision CNC turning is a major advancement over the traditional machining process, as it provides accuracy never seen before in history. The technology uses synchronized multiple-axis machining to deliver precision in the micrometer range.
1. Fundamental Technological Principles
The secret behind precision CNC turning lies in its digital control technology, which interprets the CAD drawing to produce precise mechanical movements. Conventional turning relies on human expertise, whereas precision CNC turning uses closed-loop feedback control to monitor and adjust turning parameters in real-time. The automatic system increases precision and eliminates the chances of errors as would be the case when using human expertise.
2. Accuracy and Capability Comparison
While conventional turning methods can provide a tolerance value of ±0.01mm, precision CNC turning retains a tolerance value within ±0.005mm with each production run, and such a high degree of precision is essential, especially within the production of medical devices and aero-components, as surface integrity plays a major role in determining the performance. The ability to maintain such high precision across production volumes vindicates the technology’s superiority over the conventional process.
3. Application Scope and Industry Adoption
The integration of precision CNC turning has revolutionized manufacturing in high-value industries such as the automotive, medical, and aerospace sectors. Its ability to machine exotic materials such as titanium alloys and engineering plastics précisely gives it an advantage in manufacturing high-value products. The integration of CNC turning in manufacturing indicates an advancement in manufacturing beyond the limitations of traditional manufacturing techniques.
In What Ways Can Advanced CNC Turning Machines Be Used to Obtain Micron-Level Tolerance
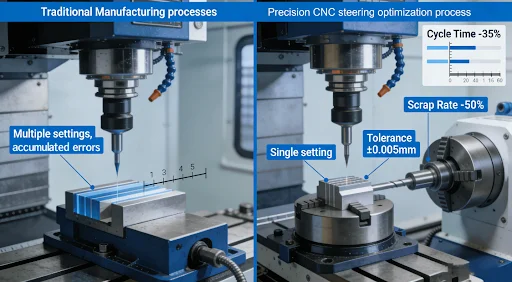
The ability to manufacture to micron-level accuracy involves complex interactions among precision engineering, environmental control, and advanced computer algorithms. Contemporary CNC turning machines utilize many technological advancements that work together to provide high accuracy across all stages of manufacturing.
- Machine Tool Design and Stability: The starting point for precision is the rigidity and thermal management of the machine tool. High-precision CNC lathes feature rigid bodies and linear motion guides that reduce vibration at high speeds. At the same time, cooling systems are installed to keep the temperature of the equipment’s critical components constant and prevent thermal expansion that could impair precision.
- Control Systems and Real-Time Compensation: In more sophisticated control systems, feedback processes operate in real time alongside compensation algorithms. High-resolution encoders track the position of tools multiple thousands of times per second, while sophisticated software algorithms compensate for any tool wear and temperature variations. This compensation enables the process to continuously maintain dimensional accuracy within tolerances, thereby overcoming variables inherent to conventional machining.
- Environmental and Operational Factors: Micron-level accuracy requires prudent management of operational and environmental parameters. Temperature-controlled manufacturing environments, vibration-isolation foundations, and correct material handling practices all play their parts in this regard. It can also be very important to replicate the correct machine setup techniques to ensure the maximum benefit of this technology is derived.
What Are the Key Processes in CNC Turning for High-Precision Components?
High-precision components are manufactured through an elaborate series of processes, each affecting the end product’s dimensions. Knowledge of these processes is crucial in obtaining successful results in precision turning.
1. Material Selection and Preparation
The process begins with material choices determined by function and manufacturing factors. The material, whether stainless steel or an engineering plastic, must also be assessed based on its machinability. Other factors to consider include cutting to size, stress-relief processes, and a specific datum for proper material setup.
2. Machining Process Optimization
The machining operation consists of intricate roughing and finishing operations. The cutting force and heat flow are optimized through high-quality cutting path algorithms. The cutting tools and their settings are properly considered to optimize surface finish and accuracy. The turning-milling operations done in a single setup ensure that there are minimal errors during handling, and the geometric constraints between the features are maintained.
3. Quality Verification and Process Validation
All production steps have thorough inspection plans to check for specification compliance. In-process inspection with touch probes and lasers provides immediate feedback, and final inspection with CMMs provides thorough dimensional analysis. The above processes work together to ensure that components meet the stringent standards required for precision applications. This CNC precision turning parts guide can also be consulted when optimizing the turning process for thin-walled parts to avoid deformation issues.
Ways & Methods to Achieve Effective Quality Control in CNC Turning.

The installation of effective quality control systems plays a crucial role in achieving zero-defect manufacturing through precision CNC turning. This strategy involves the use of measurement technologies and statistical analysis techniques.
- Implementation of Statistical Process Control: The starting point of a proper quality control program is Statistical Process Control (SPC) and how it governs the production process. By identifying key parameters, such as dimensional variation and surface finish deviations, manufacturers can take timely corrective actions to reduce the risk of defects. SPC applies statistical methods to monitor process performance, detect variation early, and reduce scrap and rework, enabling advanced statistical control systems to maintain real-time control over manufacturing operations.
- Advanced Measurement & Inspection Technologies: Modern quality control incorporates highly advanced inspection tools such as optical comparators, vision inspection systems, and 3D scanning instruments. The incorporation of on-machine probing systems enables direct dimensional verification without removing the parts from the machining environment. Such systems, together with calibration procedures, ensure that measurement accuracy is sufficient to support precise machining of turned parts.
- Quality Management System Certification: Compliance with international standards like ISO 9001 certification helps ensure quality management in an organized manner. Obtaining the certification also requires an established procedure for each part of the manufacturing process, from the receipt of materials to the final inspection. All these elements help ensure quality in every aspect since quality is in every aspect.
What Role Does Digital Transformation Play in Enhancing CNC Turning Efficiency?
Digital transformation has caused major upheaval in the field of precision CNC turning and has introduced data-driven decisions and networked systems to make manufacturing more efficient. The challenge in conventional manufacturing has thus been met and exceeded in modern CNC turning machines.
1. Industrial IoT & Data Analytics
The application of Industrial Internet of Things technology enables complete observation of the machining process through networked sensors. The technology collects enormous amounts of data regarding the machine’s operation, the condition of the tools, and the working environment. Advanced data analytics are used to analyze the data and optimize the process, thereby reducing unplanned downtime.
2. Digital Twin Technology & Simulation
Digital twin technology enables the creation of virtual models of the machining process, which can be used to optimize it before the process actually occurs. With virtual models, predictions can be made about the effects of parameter modifications, enabling process optimization without consuming resources. Digital twin technology also enables virtual training and validation of procedures.
3. Automated Workflow Integration
The new manufacturing plants use a seamless flow process that integrates design, planning, manufacturing, and quality testing. Machines automate tool changes and inspections in manufacturing, and digital documentation helps ensure that all processes are traceable. This degree of process integration, according to ASME Y14.5 for geometric dimensioning, does not create silos for knowledge and ensures EOE is optimized.
Ways for Manufacturers to Choose a Trustworthy Partner for Precision Turning Services
To choose a suitable manufacturing partner, it is necessary to assess the company’s capabilities and qualities. This will ensure the manufacturing company has access to the precision turning services necessary for their application.
- Technical Capability Assessment: A thorough analysis of a partner’s technical infrastructure would necessarily include assessments of machine tools, control capabilities, and the accuracy of measuring instruments. It would also be important for short-listed suppliers to have working experience with similar material types and component sizes. It would necessarily involve assessing the supplier’s ability to process the anticipated volume of orders.
- Quality System Verification: Quality management system verification exceeds simple quality system certification and scrutinizes the application of quality principles in day-to-day operations. Quality assessment covers the evaluation of quality record-keeping, calibration, and corrective procedures. Companies must analyze procedures and strategies of potential collaboration partners to handle non-conforming materials and mechanisms for continuous improvement, ensuring quality is of primary significance in the collaboration.
- Strategic Partnership Considerations: The selection process should assess operational cooperation and the potential for continuous improvement. The partners should express openness to consistently developing and improving each other’s performance. The best partners should feel like an extension of the manufacturer’s operations and add value to both parties through technical knowledge and process improvements.
Conclusion
Professional CNC turning services involve a holistic approach towards meeting various challenges in modern manufacturing, as it uses innovative technologies, strict processes, and systematic methodologies associated with quality. The adoption of digital transformation strategies further improves efficiency, ensuring manufacturers’ readiness to respond to market requirements while containing costs.
The road towards manufacturing excellence demands a commitment to continuous improvement and the creation of strategic partnerships that efficiently utilize specialized knowledge. Manufacturing engineers can shift their operations to new quality levels by implementing the principles and practices highlighted in this article.
FAQs
Q1. What is the generally accepted tolerance for precision CNC turning?
A:Precision CNC turning maintains an accuracy of ±0.005 mm, with rounding errors limited to 0.003 mm. Modern machines achieve this level of precision by adhering to global manufacturing standards and using real-time compensation techniques.
Q2: What is the role of CNC turning quality control in preventing defects in a mass production setup?
A: Current advanced quality control systems include the use of statistical process control and comprehensive inspection procedures conducted through the use of coordinate measuring machines. With this approach, defects are detected through data, and the scrap rate remains below 0.1% of total production.
Q3: What materials are generally suitable for making high-precision turned components?
A: Materials like titanium alloys, stainless steel, and engineering plastic provide optimal properties for precision turning. The choice depends on requirements related to intended use and properties such as strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability.
Q4: How can digital transformation lower costs for CNC turning processes?
A: Digital technologies are able to optimize cutting data, provide predictive maintenance, and simplify production processes, thus reducing cycle times by as much as 30% and energy use as a result of increased efficiency, without sacrificing quality.
Q5: What are the necessary certifications for a precision turning supplier?
A: Trustworthy suppliers should also be able to provide ISO 9001 quality management system certification and specializations in their own fields, such as the automotive parts supply domain described in IATF 16949 or aerospace parts in accordance with AS9100D.











